What is ECG ?
 |
The heart is divided into four chambers:
Each chamber has a sort of one-way valve at its exit that prevents blood from flowing backwards. When each chamber contracts, the valve at its exit opens. When it is finished contracting, the valve closes so that blood does not flow backwards. |
| The Body is an electric system
Have you ever wondered what makes your heart beat? How does it do it automatically, every second of every minute of every hour of every day? The answer lies in a special group of cells that have the ability to generate electrical activity on their own. These cells separate charged particles. Then they spontaneously leak certain charged particles into the cells. This produces electrical impuses in the pacemaker cells which spread over the heart, causing it to contract. These cells do this more than once per second to produce a normal heart beat of 72 beats per minute |
Our service can recognize 90% common heart disease ECG
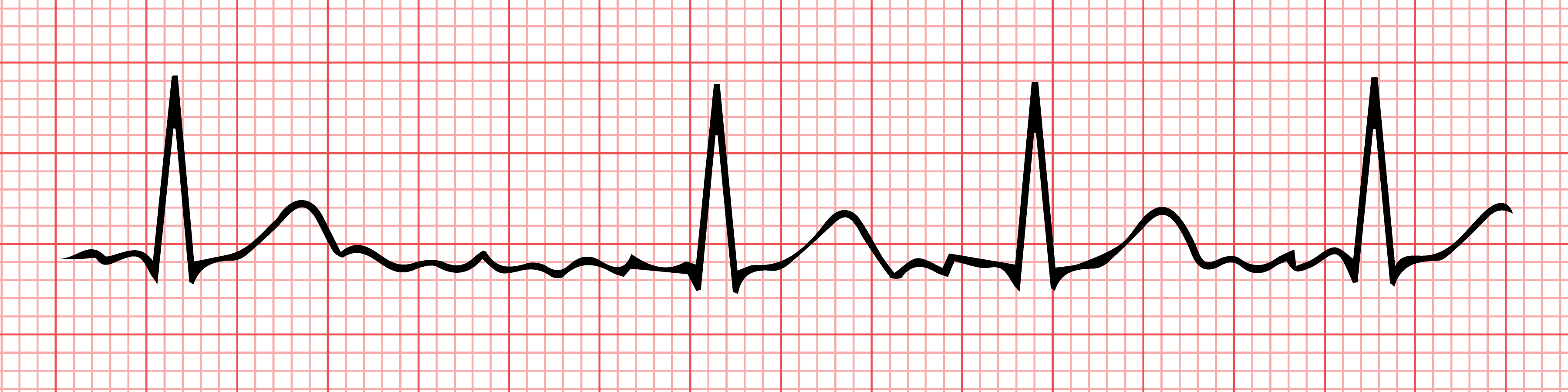
| Normal heart ECG |
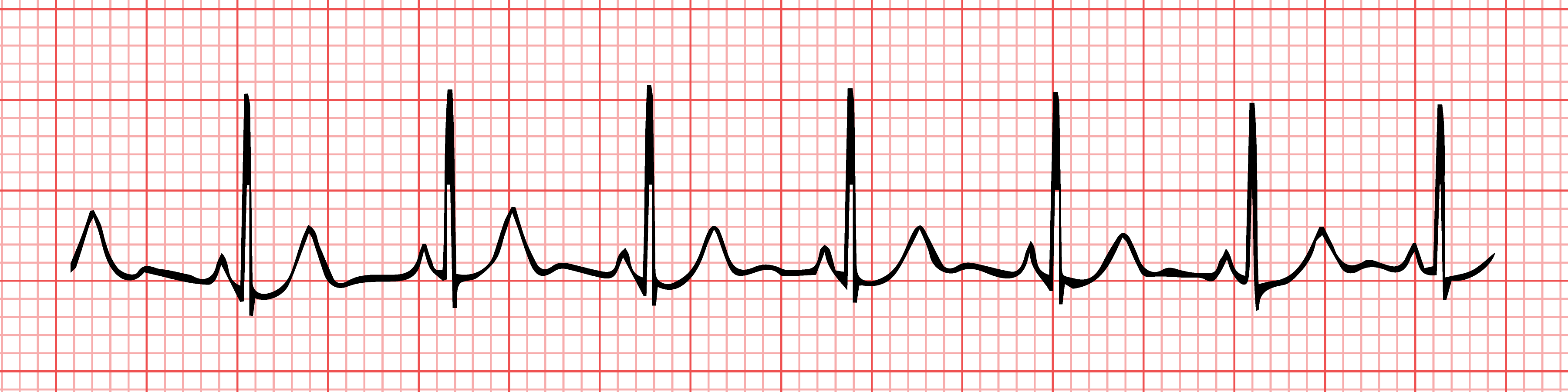 |
| Atrial Fibrillation Irregular and often rapid heart rate that can increase your risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. |
 |
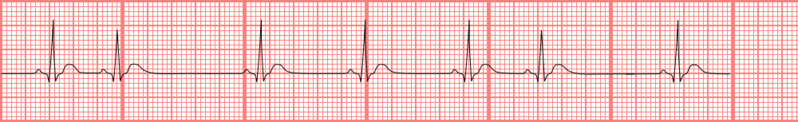
| Premature ventricular contraction (PACs) Premature arterial contractions, also known as atrial premature complexes (APC) or atrial premature beats (APB), are a common cardiac dysrhythmia characterized by premature heartbeats originating in the atria. |
 |
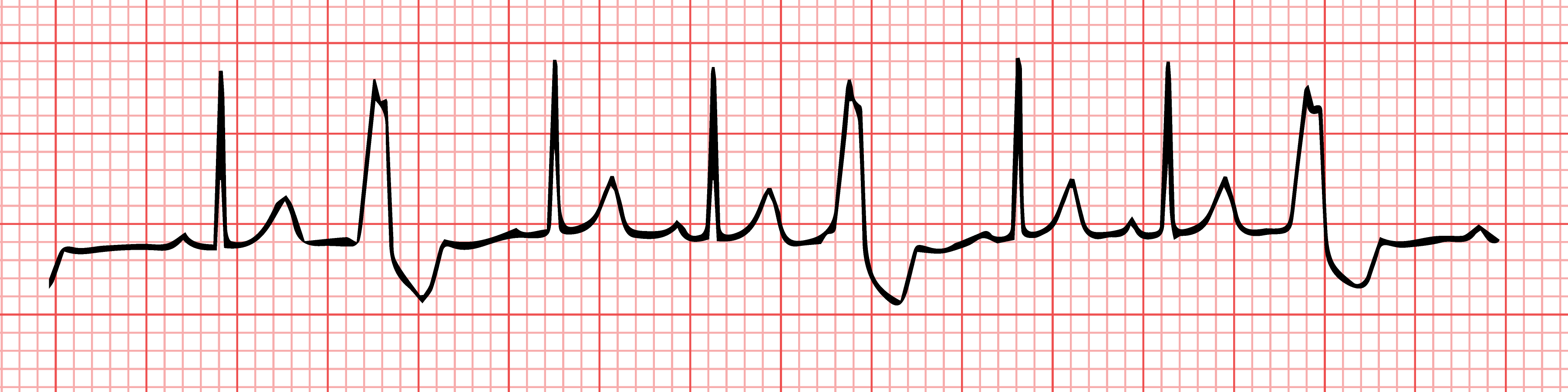
| Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are extra, abnormal heartbeats that begin in one of your heart’s two lower pumping chambers (ventricles). These extra beats disrupt your regular heart rhythm, sometimes causing you to feel a flip-flop or skipped beat in your chest. |
 |
| Sinus Bradycardia Sinus bradycardia is a sinus rhythm with a rate that is lower than normal. In humans,bradycardia is generally defined to be a rate of under 60 beats per minute. |
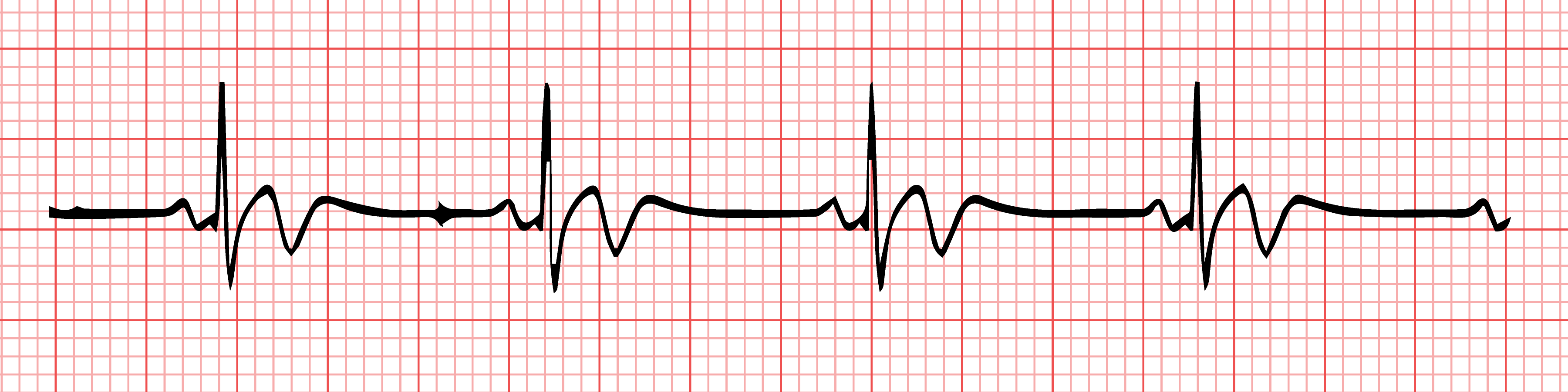 |
| Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a type of regular and fast heart rate that arises from improper electrical activity in the ventricles of the heart. |
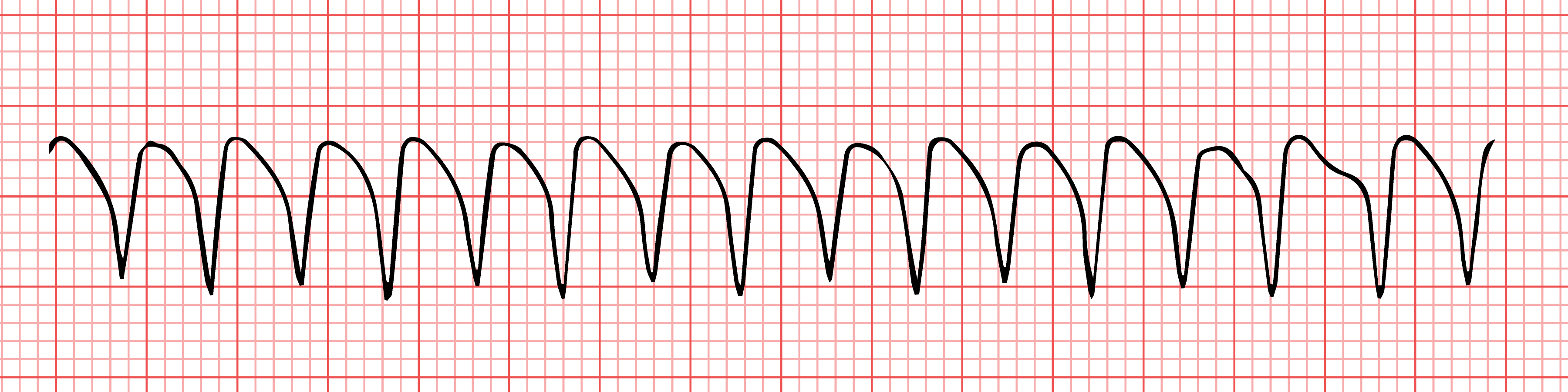 |
